Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Aihara, Jun; Hojo, Kiichi; Furuno, Shigemi*; Shimura, Kenichiro; Hojo, Tomohiro*; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Motohashi, Yoshinobu*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 242(1-2), p.441 - 444, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.84(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Aihara, Jun; Hojo, Tomohiro*; Furuno, Shigemi*; Ishihara, Masahiro; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Hojo, Kiichi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 241(1-4), p.559 - 562, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)Silicon carbide (SiC) specimens prepared for the TEM (transmission electron microscope) observation were amorphized with 30keV Ne or 4.5keV He ion irradiation at room temperature and successively annealed at 1273K in the TEM. Ne and He were selected as irradiation ion species to change the concentration of implanted rare gas atoms. The energy and flux of these ion species were selected in order to get similar dpa depth profiles and dpa rates based on TRIM calculation. In this condition, peak ion implantation of He was estimated to be about 5 times as large as that of Ne for the same peak dpa. Crystal nucleation occurred with annealing in the specimen irradiated with He up to 6.3dpa(peak), however, no crystal nucleation was observed in the specimen irradiated with Ne up to 15dpa(peak); Namely, crystal nucleation occurred with less dpa in the case of He irradiation than in the case of Ne irradiation. It was found that the concentration of implanted inert gas atom influences the crystal nucleation behavior.
Aihara, Jun; Ishihara, Masahiro; Hojo, Kiichi; Furuno, Shigemi*
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 87(6), p.1146 - 1148, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:18.37(Materials Science, Ceramics)SiC specimens were amorphized with Ne irradiation and annealed at 1273K. One specimen was annealed continuously for 60 minutes, the other was annealed repeatedly (5 minutes  10 times). Crystal nucleation in the amorphized SiC was apt to occur more in the case of repeated annealing than in the case of continuous annealing.
10 times). Crystal nucleation in the amorphized SiC was apt to occur more in the case of repeated annealing than in the case of continuous annealing.
Aihara, Jun; Hojo, Kiichi; Furuno, Shigemi*; Ishihara, Masahiro; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 8th Asia-Pacific Conference on Electron Microscopy (8APEM) (CD-ROM), p.722 - 723, 2004/06
SiC TEM specimens were irradiated with 20keV Ne+ to the fluence of 1.5x10 Ne+/m
Ne+/m at 573, 583, 598 and 683K, and successively annealed at 1273K for 30minutes. In the cases of 573 and 583K irradiation, amorphization with irradiation and crystal nucleation with annealing occurred. Coalescence of the bubbles was clearly observed in the crystal nucleated area and epitaxial growth area. In the case of 593K irradiation, partial amorphization occurred but crystal nucleation did not occur. In the case of 673K irradiation, amorphization did not occur and no change was observed after annealing.
at 573, 583, 598 and 683K, and successively annealed at 1273K for 30minutes. In the cases of 573 and 583K irradiation, amorphization with irradiation and crystal nucleation with annealing occurred. Coalescence of the bubbles was clearly observed in the crystal nucleated area and epitaxial growth area. In the case of 593K irradiation, partial amorphization occurred but crystal nucleation did not occur. In the case of 673K irradiation, amorphization did not occur and no change was observed after annealing.
Aihara, Jun; Hojo, Kiichi; Furuno, Shigemi*; Ishihara, Masahiro; Hayashi, Kimio
Journal of Electron Microscopy, 51(2), p.93 - 98, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:20.46(Microscopy)no abstracts in English
 Re(n,2n)
Re(n,2n)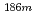 Re and
Re and 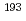 Ir(n,2n)
Ir(n,2n)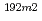 Ir at 14MeV energy region
Ir at 14MeV energy regionIkeda, Yujiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi*; Uno, Yoshitomo; Konno, Chikara; Maekawa, Hiroshi
Proc., Int. Conf. on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology,Vol. 2, 0, p.1078 - 1080, 1994/00
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, K.; Katano, Y.; Aruga, T.; Hamada, S.; Shiraishi, K.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 133-134, p.585 - 589, 1985/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:37.48(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Matsukawa, Yoshitaka*; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fujita, Shunya*; Abe, Yutaka*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Yuasa, Tomohisa*; Segawa, Tomoomi; Kato, Yoshiyuki; Kawaguchi, Koichi; Ishii, Katsunori
no journal, ,
The microwave heating denitration method is used in the spent fuel reprocessing process of the nuclear fuel cycle. Since the microwave heating method is accompanied by a transient boiling phenomenon, it is necessary to grasp the operating conditions and to clarify the mechanism of flashing and spilling in order to avoid it. In this study, by assuming the flashing model for the purpose of the clarification of the flashing mechanism by microwave heating, the flashing mechanism of instantaneous generation and growth is considered by calculating the generation frequency and volume of bubble from the visualization result at flushing. The mechanism of flashing phenomenon during microwave heating is thought that the significant flushing phenomenon occurs by the process that a large amount of nanobubbles are generated at a solid-fluid interface in a overheated liquid phase, the bubble group grows exponentially and collapses, and its internal pressure releases.
Kobayashi, Shohei*; Abe, Yutaka*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Fujiwara, Kota*; Futsuta, Akihiro*; Segawa, Tomoomi; Kawaguchi, Koichi; Ishii, Katsunori
no journal, ,
The microwave heating denitration method is used in the nuclear fuel cycle. To clarify the mechanism of flashing phenomena during microwave heating, it was focused on the frequency of bubble nucleation in heterogeneous nucleation and considered the bubbles generated in the solution. From the visualization observation results, it was verified that a new bubble was generated below the single bubble. The bubbles generated at the gas-liquid interface are considered to be caused by heterogeneous nucleation. Moreover, the calculation results revealed that bubbles were generated at a large contact angle. It is suggested that many bubbles are generated at the gas-liquid interface, and many bubbles generated by heterogeneous nucleation in the superheated liquid phase influence the generation of flashing.